Introduction
The California Cap-and-Trade Program launched in 2012, marking the beginning of its tracking system for allocation, auction distribution, and trading of compliance instruments. Compliance obligations commenced in January 2013, covering nearly 80% of the state's GHG emissions. The program is managed by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) and has been part of the Western Climate Initiative (WCI) since 2007. In January 2014, California formally linked its program with Québec’s. The program is central to meeting California’s ambitious goals to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to 1990 levels by 2020 (which it met in 2016), 40 percent below 1990 levels by 2030, and 80 percent below 1990 levels by 2050.
Scope
The program covers approximately 450 facilities across the power, industrial, transportation, and buildings sectors. Entities are required to surrender allowances for all covered emissions. This includes large industrial facilities, power plants, electricity imports, and CO₂ suppliers with annual emissions exceeding 25,000 tCO₂e. It also includes natural gas suppliers, fuel oil blenders, and liquefied gas suppliers. Entities with lower emissions may choose to participate voluntarily, provided they comply with requirements for registration, reporting, verification, and adherence to obligations. Emissions from imported electricity are calculated using a default emissions factor.
All covered entities are required to report emissions annually, and these reports must be verified by a third party. Both covered entities and other participants must register with CARB to take part in allowance auctions.
Allowances
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) establishes a cap on total permissible greenhouse gas emissions, with each allowance representing one metric ton of carbon dioxide equivalent. Allowances are distributed through a combination of free allocation, free allocation with consignment, and auctions.
Industrial facilities receive free allowances based on product-specific benchmarks and leakage risk, with a 100% assistance factor in place through 2030 to prevent carbon leakage. Utilities also receive free allowances on behalf of their ratepayers, some of which are consigned for sale at auctions. Approximately 70% of allowances are offered at auction, and any unsold allowances are moved to reserves if prices exceed the minimum for two consecutive auctions. Revenue generated from these auctions is deposited into the state’s Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund.
The annual cap decreases over time, reducing the number of allowances issued each year. This declining cap, combined with an increasing auction reserve price, provides a consistent carbon price signal to drive greenhouse gas emissions reductions.
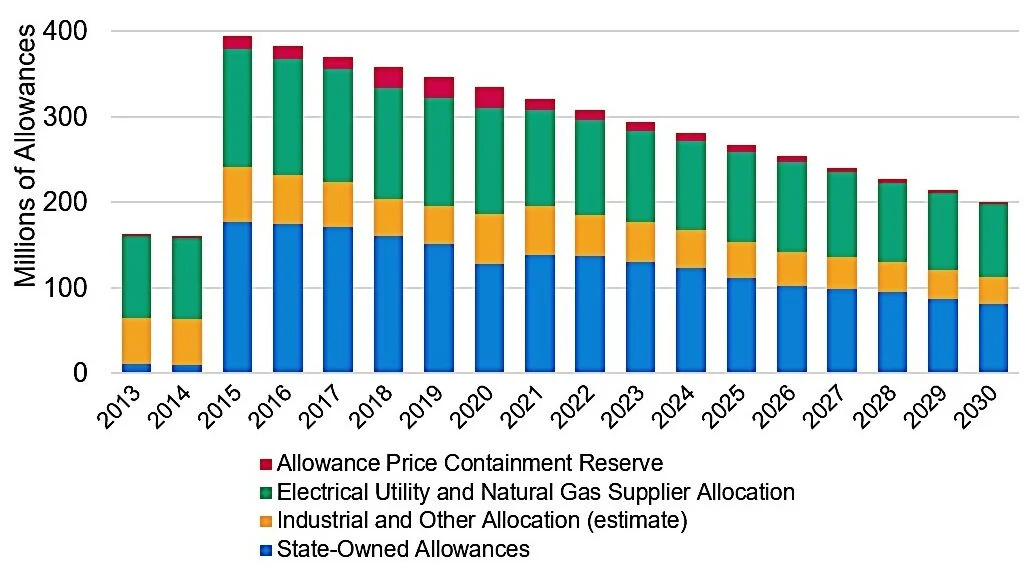
California ETS Allowances Distribution. Source: Carboncredit.com
Recent Updates
ARB and the Government of Québec have worked together on updates to the linked carbon market. Key amendments include:
- Removal of at least 180 million allowances from the 2026-2030 annual budgets to align with the 2022 Scoping Plan and AB 32 Greenhouse Gas Inventory updates, and up to 265 million allowances removed from the 2026-2045 budgets.
- A one-time increase in cost-containment prices to better reflect the federal social cost of carbon.
- Updates to triggers for corporate association groups to deter market manipulation.
- Clarifications on offset protocols for Livestock Projects, Mine Methane Capture Projects, and Ozone Depleting Substances Projects.
- Adjustments to allowance allocation for electrical utilities and selected industrial sectors based on updated data.
- Modifications to reflect the Extended Day Ahead Market being developed by CAISO.

 Launch of the Green Banking Component under the Technical Assistance Project on Expanding Inclusive and Climate Finance
Launch of the Green Banking Component under the Technical Assistance Project on Expanding Inclusive and Climate Finance
 Meeting to propose the implementation of the Letter of Intent for the National Green Carbon Action Partnership Program (NBCAP)
Meeting to propose the implementation of the Letter of Intent for the National Green Carbon Action Partnership Program (NBCAP)